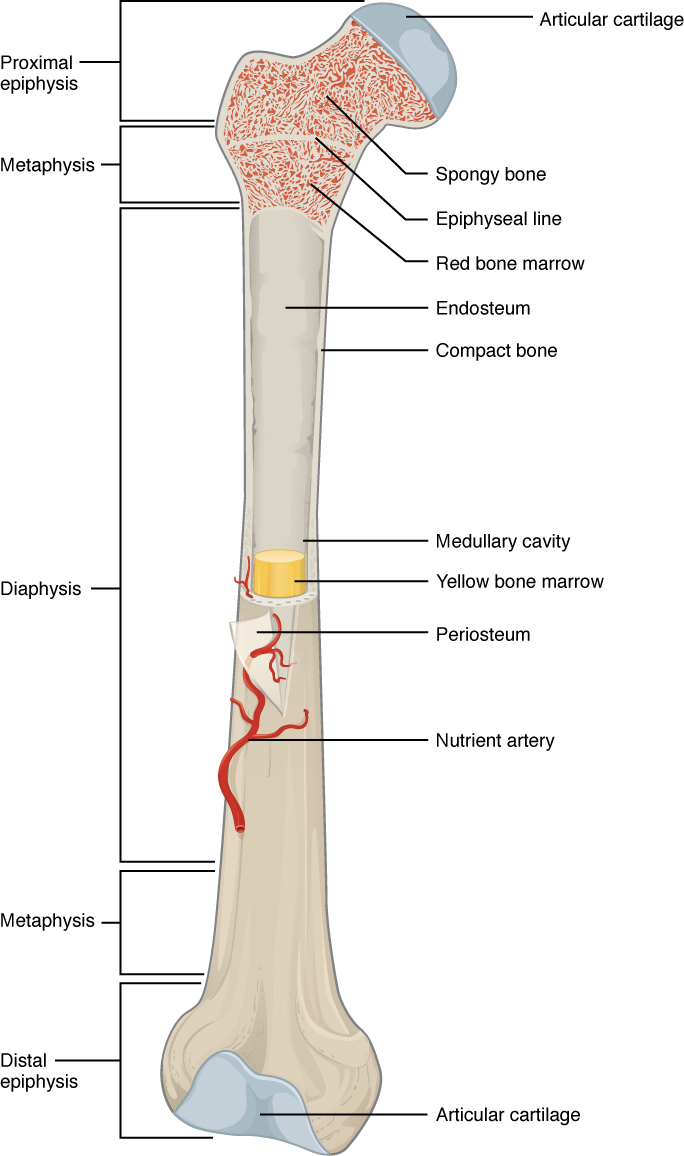
The internal structure of a long bone is revealed by a longitudinal section. This is covered by a membrane of connective tissue called the periosteumBeneath the cortical bone layer is a layer of spongy cancellous boneInside this is the medullary cavity which has an inner core of bone marrow it contains nutrients and help in formation of cells made up of.
Bone Structure Anatomy And Physiology
The radius or the radial bone is found in the forearm.
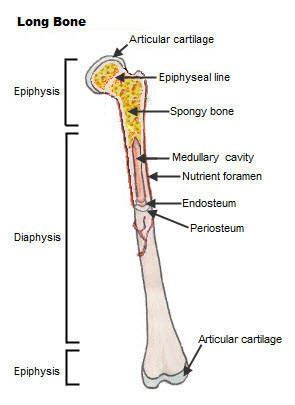
. The humerus is the long bone structure found in the upper arm. The ulna is the bone found next to the radius of the forearm. The diaphysis is covered protected by a fibrous connective tissue membrane.
What is the structure of a long bone. Compact bone in the diaphysis of a long bone forms a semirigid tube which has a hollow chamber called the medullary cavity that is continuous with the spaces of the spongy bone. Inside the diaphysis is the medullary cavity which is filled with yellow bone marrow in an adult.
The diaphysis and the epiphysis. Each osteon consists of lamellae which are layers of compact matrix that surround a central canal called the Haversian canal. The diaphysis and the epiphysis Figure 631.
The diaphysis is the hollow tubular shaft that runs between the proximal and distal ends of the bone. They are composed mostly of compact bone and are roughly cylindrical in shape with enlarged ends filled with spongy bone. Expert Answer A long bone has two main regions.
The hollow region in the diaphysis is called the medullary cavity which is filled with yellow marrow. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. Medullary cavity bone marrow.
The Structure of a Long Bone. Epiphysis epiphyseal plate metaphysis diaphysis medullary cavity articular cartilage and periosteum. Key Skeletal System Facts.
The femur or thigh bone is the lone largest bone of the upper legs. It consists of thin rods or plates called trabeculae trah-bek-u-le that form a meshlike framework containing numerous spaces. This is how a long bone grows.
Diaphysis or shaft makes up the most of the bones length is composed of compact bone. Long bones are the most common bones found in the human body. Spongy trabecular bone forms the internal structure of the epiphyses and the internal surface of the diaphysis wall.
The walls of the diaphysis are composed of dense and hard compact bone. The diaphysis and the epiphysis. The bone contains a central medullary cavity that serves as the center for bone marrow production.
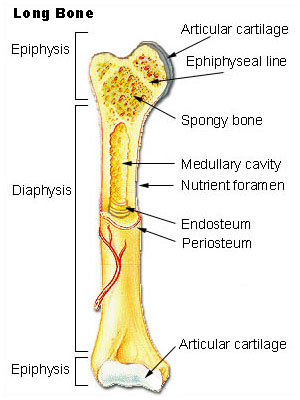
Anatomy and Types of Long Bones There are six types of long bone structures in the body. Epiphysis From the Greek meaning to grow upon this spongy bone tissue is spherical in shape and is located at both the distal and proximal end of a long bone. The axial skeleton includes the bones of the.
The bones typically consist of a long shaft called the diaphysis and two wider extremities on the ends called epiphyses. There are three types of cells that contribute to bone homeostasisOsteoblasts are bone-forming cell osteoclasts resorb or break down bone and osteocytes are mature bone cells. In a long bone this is normally found at either end of the bone in flat or irregular bones it is a thin layer found just inside the compact bone.
Compact and spongyThe names imply that the two types differ in density or how tightly the tissue is packed together. They are aligned parallel to the long axis of the bone. A long bone has two parts.
Interestingly compact bone constitutes up to 80 of the bones weight with spongy bone making up the additional 20 despite its much larger surface area. Describe all general structures of the bone and include their functionspurposes. As part of your Level 2 Anatomy and Physiology Exam you need to be aware of the structure of a long bone and know the.
A long bone has two main regions. Structure of Bone Tissue. Gross Anatomy of Bones.
While the name suggests a larger size of bone bones such as the metacarpals in the fingers are classified as long bones. The long bones are made of spongy bone at the epiphyseal ends bone marrow cavity within the diaphysis and cortical bone all the way around. The diaphysis and the epiphysis.
The diaphysis is the tubular shaft that runs between the proximal and distal ends of the bone. These bones tend to support weight and help movement. Structure of a Long Bone - Gross Anatomy.
A thin layer of cells called the endosteum lines these areas and a specialized type of soft connective tissue called marrow fills them. The outer shell of the long bone is made of cortical bone also known as compact bone. A long bone has two parts.
Also include the structures of compact and spongy bone. Central not spongy. These are mostly compacted bone with little marrow and include most of the bones in the limbs.
There are two types of bone tissue. You need to know about Axial and Appendicular Skeletons for your exam. Structure of Long Bones.
The major parts of a long bone are. The diaphysis is the hollow tubular shaft that runs between the proximal and distal ends of the bone. The walls of the diaphysis are composed of dense and hard compact bone.
The diaphysis is the tubular shaft that runs between the proximal and distal ends of the bone. Describe the structure of a long bone diaphysis metaphysis epiphyses articular cartilages epiphyseal plates or epiphyseal lines medullary cavity bone marrow periosteum and endosteum Diaphysis Shaft or body Metaphysis Contains the epiphyseal plate in a growing bone Epiphysis Is the end Articular cartilages Is a thin layer of cartilage. Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area.
Bones protect the various organs of the body produce red and white blood cells store minerals provide structure and support for the. You wont find any. Osteons are cylindrical structures that contain a mineral matrix and living osteocytes connected by canaliculi which transport blood.
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the vertebrate skeleton. What is the structure of a typical long bone. The typical human skeleton consists of 206 bones in adults.
The hollow region in the diaphysis is called the medullary cavity which is filled with yellow marrow.

Bone Structure Anatomy And Physiology I

Seer Training Classification Of Bones
0 Comments